
Outbound Logistics
In supply chain management, outbound logistics emerges as a critical step that bridges the gap between a company’s operations and its customers. This article delves into the realm of outbound logistics, exploring its significance, key components, and strategies to streamline this vital process.
Understanding Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics refers to the management of goods and information as they flow from a company’s production facilities to the end consumer. It encompasses a series of interconnected activities aimed at ensuring the timely and cost-effective delivery of products while maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction.
Key Components of Outbound Logistics
- Order Processing and Fulfillment: Efficient outbound logistics begins with accurate order processing. This involves receiving, validating, and processing customer orders, followed by proper picking, packing, and shipping of products. An optimized order fulfillment process reduces lead times and enhances customer experience.
- Warehousing and Inventory Management: Proper warehousing and inventory management are crucial for maintaining a smooth outbound logistics flow. Utilizing advanced inventory management systems helps businesses keep track of stock levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize carrying costs.
- Transportation and Distribution: The transportation phase involves selecting the appropriate mode of transportation (road, rail, air, or sea) based on factors like distance, urgency, and product characteristics. Leveraging efficient route planning and tracking systems optimizes delivery routes, reduces transit times, and lowers transportation costs.
Strategies to Enhance Outbound Logistics
- Integrated Technology Solutions: Implementing robust technology solutions such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) streamlines processes by providing real-time visibility, automating tasks, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Collaborative Partnerships: Building strong relationships with carriers, suppliers, and distributors enhances collaboration and information sharing. This enables businesses to respond swiftly to changes in demand, reduce lead times, and enhance overall supply chain agility.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging data analytics helps identify patterns, trends, and potential bottlenecks in the outbound logistics process. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions and continuously improve their logistics operations.
Outbound Logistics Process Flow
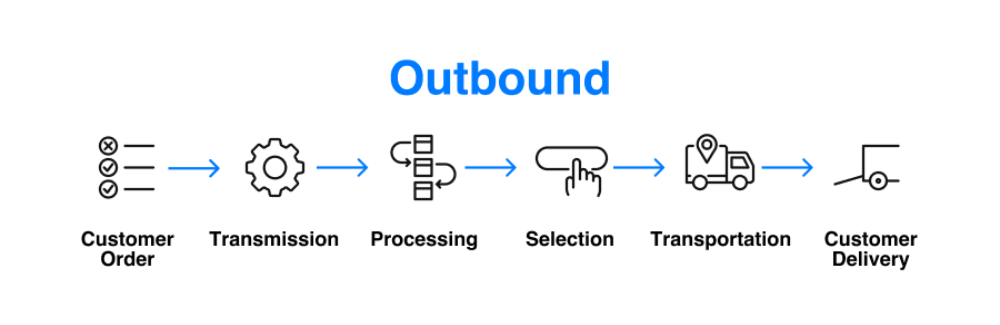
Benefits of Optimized Outbound Logistics:
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:
Streamlined outbound logistics to ensure that products reach customers in a timely manner and in optimal condition. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to higher satisfaction rates, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Reduced Costs:
Effective outbound logistics can lead to reduced transportation and distribution costs through better route planning, load optimization, and efficient use of resources. Minimized lead times also contribute to cost savings.
Inventory Control and Demand Forecasting:
By maintaining an efficient outbound logistics process, businesses can accurately gauge demand patterns and adjust inventory levels accordingly. This prevents stockouts and excess inventory, leading to improved cash flow and better resource allocation.
Market Expansion:
A well-managed outbound logistics network can open doors to new markets and regions. By ensuring reliable and efficient delivery, businesses can reach customers beyond their immediate vicinity, expanding their customer base.
Brand Reputation:
Timely and accurate deliveries contribute to a positive brand image. Customers associate dependable logistics with a well-organized and trustworthy company, thereby enhancing brand reputation.
Operational Efficiency:
An optimized outbound logistics process leads to smoother operations, reduced bottlenecks, and improved resource utilization. This, in turn, boosts overall operational efficiency and productivity.
Real-time Visibility:
Modern technology solutions provide real-time visibility into the outbound logistics process. Businesses can track shipments, monitor progress, and address any issues promptly, leading to improved decision-making.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
Modern technology solutions provide real-time visibility into the outbound logistics process. Businesses can track shipments, monitor progress, and address any issues promptly, leading to improved decision-making.
Difference Between Outbound & Inbound logistics
While both outbound and inbound logistics are integral components of the supply chain, they operate in distinct ways to ensure the smooth flow of materials and products throughout the entire process. Let’s delve into the key differences between these two crucial aspects:
| Differences | Inbound Logistics | Outbound Logistics |
| Focus and Direction | Primarily involves sourcing, transporting, and managing materials from suppliers to the company’s facilities for production. | Concentrates on delivering finished products from the company’s facilities to customers, distributors, or retailers. |
| Activities | Includes sourcing, purchasing, receiving, and warehousing of raw materials to support production. | Encompasses order processing, picking, packing, shipping, and distribution of finished products. |
| Inventory Management | Focuses on maintaining adequate raw material supply, reducing stockouts, and managing supplier relationships. | Aims to ensure products are available for distribution, minimize excess stock, and optimize order fulfillment. |
| Transportation Considerations | Involves selecting transport modes to bring materials to the company’s facilities, emphasizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. | Focuses on delivering products to customers or distribution points, considering speed, cost, and customer preferences. |
| Customer Interaction | Primarily involves B2B interactions with suppliers and manufacturers. | Often involves B2C interactions directly impacting end customer experiences. |
| Goal | Supports manufacturing and production processes by ensuring a steady supply of materials. | Focuses on timely delivery of the final product to customers, retailers, or distributors. |
| Example | Procuring raw materials for a car manufacturing plant. | Delivering cars from the manufacturing plant to dealerships. |
| Impact | Affects production efficiency and cost control. | Influences customer satisfaction and brand reputation. |
Conclusion:
Outbound logistics forms the backbone of a seamless supply chain, orchestrating the movement of products from production to consumption. By focusing on efficient order processing, strategic warehousing, optimized transportation, and the power of technology, businesses can elevate their outbound logistics and deliver superior customer experiences. Embracing data-driven strategies and nurturing collaborative partnerships will undoubtedly contribute to the ongoing success of any modern supply chain.
Remember, optimizing outbound logistics isn’t a one-size-fits-all endeavor; it requires a deep understanding of your business’s unique needs and a commitment to continuous improvement.
